Introduction to Venous Health
The human circulatory system is a marvel of biological engineering, with veins playing a crucial role in maintaining overall health. Veins carry deoxygenated blood back to the heart, working against gravity and relying on a complex system of valves and muscle contractions to function properly. Understanding venous health is essential for everyone, impacting our daily lives and long-term well-being.
The Anatomy of Veins
Veins are blood vessels that transport blood from various body parts to the heart. Unlike arteries, which have thick, muscular walls to handle blood pressure from the heart, veins have thinner walls and contain valves to prevent blood from flowing backward.
Types of Veins
- Superficial veins: Located close to the skin surface
- Deep veins: Found deeper within the body, surrounded by muscles
- Perforator veins: Connect superficial and deep veins
Venous Valves
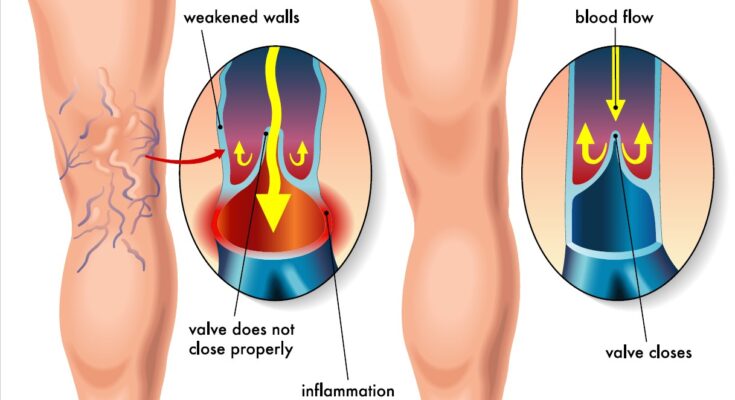
Venous valves are small, one-way flaps that open to allow blood to flow toward the heart and close to prevent backflow. They are crucial for maintaining proper blood circulation, especially in the legs, where blood must flow against gravity.
Common Venous Disorders
Several conditions can affect venous health, ranging from minor cosmetic issues to more serious medical concerns. Some of the most common venous disorders include:
- Varicose Veins
- Spider Veins
- Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
- Chronic Venous Insufficiency (CVI)
- Venous Ulcers
Varicose Veins
Varicose veins are enlarged, twisted veins that often appear on the legs and feet. They occur when the valves in the veins become weak or damaged, allowing blood to pool and cause the veins to swell. While often considered a cosmetic issue, varicose veins can sometimes cause discomfort and lead to more serious problems if left untreated.
Spider Veins
Spider veins are smaller, thread-like veins that appear close to the skin’s surface. They are typically red, blue, or purple, often resembling a spider’s web or tree branches. While generally harmless, some people may seek treatment for cosmetic reasons.
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
DVT is a serious condition characterized by the formation of blood clots in deep veins, usually in the legs. These clots can be dangerous if they break loose and travel to the lungs, causing a pulmonary embolism. DVT risk factors include prolonged immobility, certain medical conditions, and genetic predisposition.
Symptoms of Venous Disorders
Recognizing the symptoms of venous disorders is crucial for early detection and treatment. Common symptoms include:
- Aching or heavy feeling in the legs
- Swelling in the legs or ankles
- Visible varicose or spider veins
- Skin discoloration or ulcers
- Itching or burning sensation in the affected area
- Leg cramps, especially at night
Suppose you experience persistent symptoms or are concerned about your venous health. In that case, it’s essential to consult with vein specialists in Utah or other qualified healthcare providers who can provide expert diagnosis and treatment options.
Diagnostic Methods for Venous Disorders
Accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment of venous disorders. Healthcare providers use various methods to assess venous health and identify potential issues:
- Physical examination
- Duplex ultrasound
- Venography
- CT or MRI scans
Duplex Ultrasound
Duplex ultrasound is a non-invasive imaging technique that combines traditional ultrasound with Doppler ultrasound. This method allows healthcare providers to visualize the structure of veins and assess blood flow, making it an invaluable tool in diagnosing venous disorders.
Treatment Options for Venous Disorders
Treatment for venous disorders varies depending on the specific condition and its severity. Options range from conservative measures to more advanced medical procedures:
- Conservative treatments:
- Compression stockings
- Lifestyle changes (exercise, weight management)
- Elevation of affected limbs
- Minimally invasive procedures:
- Sclerotherapy
- Endovenous laser treatment (EVLT)
- Radiofrequency ablation
- Surgical interventions:
- Vein stripping
- Ambulatory phlebectomy
Sclerotherapy
Sclerotherapy is a popular treatment for small to medium-sized varicose veins and spider veins. The procedure involves injecting a solution directly into the affected veins, causing them to collapse and eventually fade away. Multiple sessions may be required for optimal results.
Preventing Venous Disorders
While some risk factors for venous disorders are beyond our control, there are several steps we can take to promote venous health and reduce the likelihood of developing problems:
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Exercise regularly, focusing on activities that engage the calf muscles
- Avoid prolonged periods of sitting or standing
- Elevate legs when resting
- Wear compression stockings if recommended by a healthcare provider
- Stay hydrated
- Avoid smoking and limit alcohol consumption
The Importance of Exercise
Regular exercise, particularly activities that engage the calf muscles, can significantly improve venous health. Walking, swimming, and cycling are excellent low-impact options that promote blood circulation and strengthen the muscles that support healthy vein function.
Venous Health and Overall Well-being
Maintaining good venous health is not just about preventing visible veins or avoiding discomfort; it’s an essential component of overall cardiovascular health and general well-being. Healthy veins contribute to:
- Efficient blood circulation
- Proper oxygen and nutrient delivery to tissues
- Removal of waste products from cells
- Regulation of body temperature
- Support for immune system function
Special Considerations for High-Risk Groups
Certain populations may be at higher risk for venous disorders and require special attention to maintain venous health:
- Pregnant women
- Older adults
- People with a family history of venous disorders
- Individuals with occupations requiring prolonged standing or sitting
- Those with a history of blood clots or certain medical conditions
Venous Health During Pregnancy
Pregnancy can significantly impact venous health due to hormonal changes and increased blood volume. Pregnant women are at higher risk for developing varicose veins and should take extra precautions, such as:
- Wearing maternity support hose
- Staying active with low-impact exercises
- Elevating legs regularly
- Sleeping on the left side to improve circulation
The Future of Venous Health Care
As medical technology advances, new treatments and diagnostic tools for venous disorders continue to emerge. Some promising developments include:
- Improved imaging techniques for more accurate diagnosis
- Less invasive treatment options with shorter recovery times
- Personalized treatment plans based on genetic factors
- Advanced compression garments with smart technology
- Enhanced patient education and self-management tools
Wrapping Up: The Importance of Venous Health
Understanding and maintaining venous health is crucial for overall well-being and quality of life. By recognizing the signs of venous disorders, seeking timely medical attention, and adopting healthy lifestyle habits, we can promote optimal venous function and prevent many common vein-related issues. Early intervention is key, and consulting healthcare professionals when concerns arise can lead to better outcomes and improved long-term health.