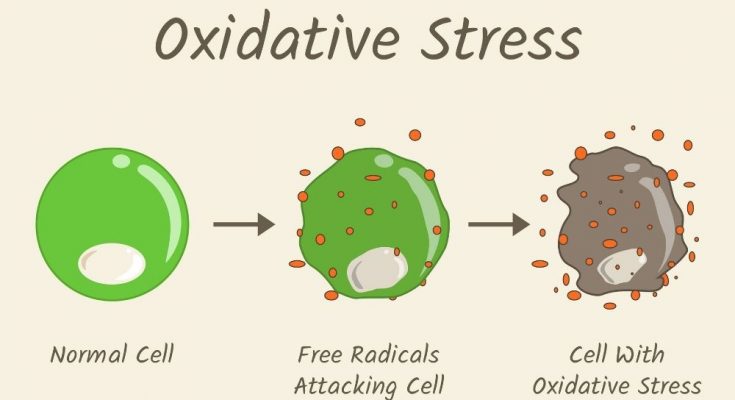
The process of aging includes a combination of separate events that happen in the body over time. Naturally, our healing abilities and general functions start to slow down, making them less effective than they were in our younger years. But, if we’re going to understand why these changes occur when they do, it’s important that we first familiarize ourselves with cellular deterioration at its core. This is what to know about oxidative stress and how you can slow it in your later years.
Oxidative Stress Wears Away at Your Cells
The first thing you should know about oxidative stress is that it occurs when the number of free radicals, or charged molecules, in your body surpasses the concentration of antioxidants. Free radicals increase the rate of damage your cells experience, causing them to die off more easily. Cells that were healthy and strong just a few years prior are now constantly under attack, and they break down much more quickly. This keeps certain areas of the body from maintaining their peak standards of health.
It Contributes to a Series of Health Conditions
Oxidative stress plays a key role in the development of a series of different health ailments as a person ages. Because these reactions take place at the cellular level, oxidative stress doesn’t just occur in one or two areas of the body. In fact, your entire system is at risk of dealing with it. A few conditions linked to oxidative stress include heart disease, diabetes, asthma, and Alzheimer’s disease. So, it’s important that you find ways to neutralize this damage wherever possible.
Several Factors Can Increase Oxidative Stress
Some of the best ways to reduce your risk of oxidative stress as you get older is to understand the environmental or lifestyle factors that can contribute to it. This way, you can reduce the potential damage by limiting your exposure to these factors. Typically, oxidative stress tends to be higher in people with obesity or diets that consist of processed foods and sugars. Smoking cigarettes, drinking alcohol, and general air pollution can also affect your body.
Glutathione Can Protect You
The most important thing to know about oxidative stress, though, is that certain substances can mitigate it. Glutathione is a natural material the body creates to protect cells from the effects of oxidative stress. It works by surrounding the cells in a barrier that blocks damage from free radicals and promotes a more effective healing process after the fact. However, the production of this molecule slows down significantly as we get older. For this reason, it’s important that you find ways to increase the glutathione in your system if you want to stay healthy in the long term.