Modern-day drug development is fascinating when you think about the deep-rooted history of medicine. A wide array of modern medicines—both over-the-counter and prescription—are inspired by nature. In fact, the first medicinal drugs came from natural sources and plants, such as roots, herbs, vines, bark, and fungi. Today’s chemical compounds that make up a pharmaceutical drug’s active ingredients are a bit different.
Until the introduction of synthetic drugs to the industry, nature’s organic pharmaceuticals were the solely available sources to alleviate humanity’s pain and suffering. All that changed during the later 19th century, when the deep curiosity and ingenuity of researchers worked together to develop safer plant chemical compounds. Here’s an overview of a few modern medicines originally derived from plants.
Morphine
Morphine—as well as other pharmaceutical opiates such as codeine—originate from the opium poppy. The opium poppy, whose scientific name is Papaver somniferous, is a medicinal plant that’s been known to humanity since ancient civilizations. The poppy’s fleshy buds, or seed pods, are sliced open to let its internal milky latex bleed out. Once this latex or gum dries, it forms raw, pure opium.
Most opiates are alkaloids, or organic compounds that can natural or synthetic. These alkaloids are the starting materials for and the most active ingredients in modern opiates. Morphine is well-known for its pain-relieving capabilities, but it is highly addictive.
Digoxin
Digoxin, or Digitalis purpurea, is another of the modern medicines originally derived from plants. Digoxin is an active ingredient that stems from theflowering plant commonly known as foxglove. It’s said to have been discovered by a doctor centuries ago after a nomad gave an herbal remedy containing foxglove to his dying patient—who recovered.
As a beneficial medication for heart failure and cardiac arrhythmias, the drug works to slow the heart rate. Only small doses are necessary, as it’s so strong that overdosing is a feasible possibility.
Penicillin
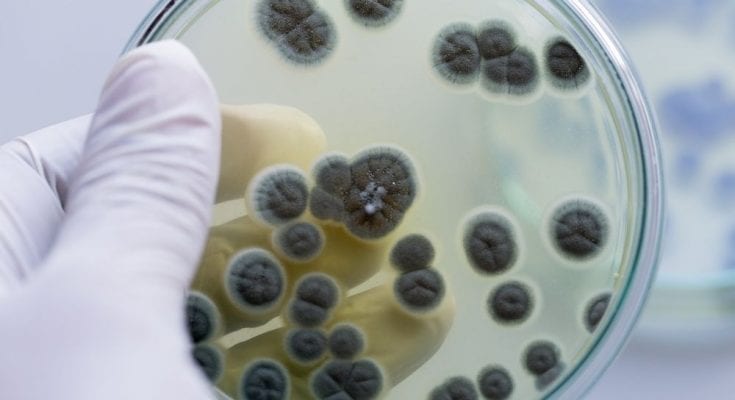
The introduction of this moldy type of drug was a complete world-changer for modern medicine. Penicillin was the first outright antibiotic solution to be discovered. Interestingly enough, it was accidentally found after a scientist left a petri dish of bacteria out overnight. Penicillin mold is undeniably one of the most common forms of mold, as it’s easily suited to grow in the right clammy conditions.
Penicillin can capably combat a range of bacterial infections, with synthetic chemistry providing solutions to resistant strains. Where would we be without these technological and medical advancements? Over time, humans have been able to take clues from nature to produce effective answers with their innovation, cleverness, and brainpower.