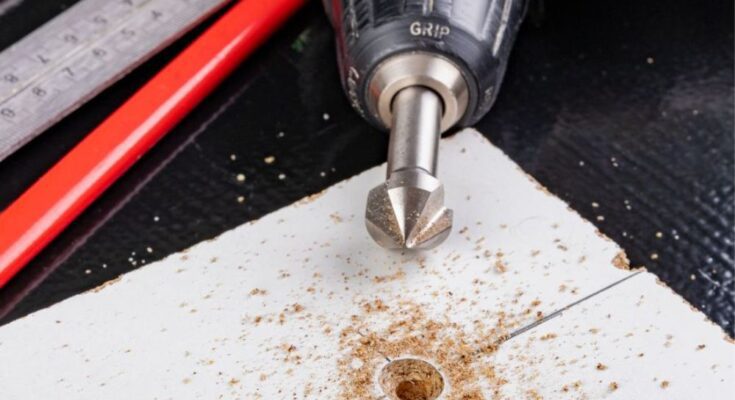
If you’re just starting out in metal or wood fabrication, it’s important to learn as many techniques as possible. One of these techniques is pre-drilling your holes for inserting screws into a project. These pre-drilled holes are called pilot holes because they help point your screw in the right direction. Discover everything you need to know about drilling pilot holes.
Why You Need a Pilot Hole
As we mentioned above, a pilot hole is a hole that you make ahead of time to make drilling screws easier. If you’re drilling into metal without a pilot hole, the vibrations from the drill can make your bit wander off the mark, causing your screw to end up in the wrong position. In a piece of wood, drilling screws without a pilot hole can make the wood split, ruining your project.
How To Drill a Pilot Hole
To make a pilot hole in your workpiece, you first need a drill bit that’s intended to cut either wood or metal, depending on the material you’re working with. Next, you should make sure you have a drill bit that’s the same diameter as your screws, not including the threads. Threads are what we call the ridges on the outside of the screw. After you mark your hole locations, you can make your pilot holes.
Drilling Pilot Holes in Wood
When making pilot holes in wood, there are slightly different rules for choosing your drill bit size. For softwoods, it’s better to choose a bit that’s slightly smaller than the diameter of your screws. With hardwood, you’ll want to make your holes slightly bigger than the screws.
Tapping Your Pilot Holes
Sometimes, you’ll need to use nuts and bolts to secure pieces instead of screws. This is when you need to tap your holes. Tapping is one of the most common vertical drill press operations, and it adds ridges to the inside of a pre-drilled hole. This allows you to insert nuts instead of screws, which make their own ridges.
And that’s it! That’s everything you need to know about drilling pilot holes. Know that practice makes perfect, and it’s always best to measure your holes twice before drilling.