
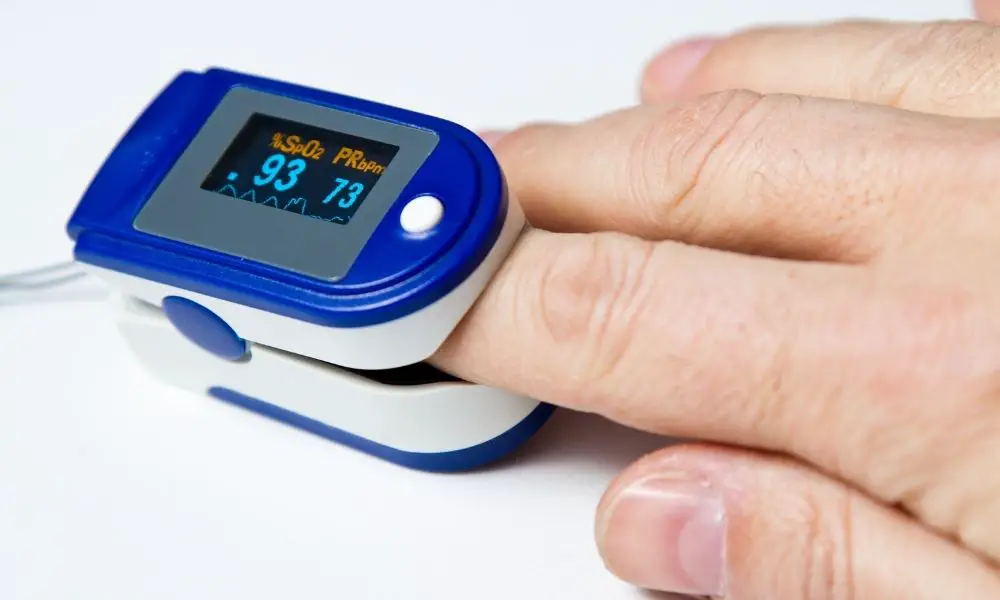
Pulse oximetry is well-known in the wide world of modern health care. Pulse oximetry refers to a non-invasive testing method that measures blood oxygen levels. Medical professionals use innovative pulse oximeter devices to monitor and evaluate the oxygen saturation levels in an individual’s blood.
Here is a look at the clinical benefits of pulse oximetry: a brief history. Let’s examine the importance of this critical testing method and diagnostic tool today.
Pulse oximetry is significant for clinical applications due to its ability to measure the effectiveness of oxygen-carrying blood. Pulse oximeters strategically evaluate how well the heart pumps and distributes oxygen throughout the body. Known by some as the fifth vital sign—alongside pulse, temperature, blood pressure, and respiratory rate—a healthy oxygen saturation level is typically at or above 95 percent.
How did this testing first begin? In 1974, Japanese engineer Takuo Aoyagi invented a small, finger clip-on device that utilized absorption principles to monitor the percentage of oxygen-saturated hemoglobin. This achievement was an accumulation of years of formational research and innovation. The clinical benefits of pulse oximetry devices have saved countless lives since.
The totality of modern-day pulse oximeters is based on Dr. Aoyagi’s original principles and his major contribution to medical science. Thanks to his efforts—and those on his team—this type of quick yet accurate wellness monitoring is possible without the need to draw blood.
The detection of oxygen saturation levels with pulse oximetry has countless clinical applications. Pulse oximeter use is mainly beneficial for those who have chronic/current conditions or illnesses that affect blood oxygen levels. With accurate readings, professionals and patients can monitor saturation over time, be readily alerted to severely low levels, and assess the possible need for supplemental oxygen use.
As an integral addition to modern medicine, pulse oximetry has played a significant monitoring role in outpatient, inpatient, and home healthcare settings. This is especially true over the last few years due to the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic. With the right knowledge, patients can use at-home pulse oximeter readings to identify whether their heart and lungs are currently supplying adequate oxygen.
All things considered, these oxygenation readouts are a general estimation. Yet, with the proper approach and application, pulse oximetry provides precise information to detect any rapid changes in the status of a patient. No other medical device or technique can provide this valuable clinical data with the same efficiency and convenience.
A lot of the time, renting an excavator is a cheaper option for building and…
Craft a nurturing nursery with DIY projects and clever storage tips while preparing your heart…
Discover how paid surveys work, if they're legitimate, tips for success, and realistic earnings expectations.…
Making your business ADA-compliant is much simpler than you realize and it’s also nonnegotiable, including…
Maintain your diesel turbocharger with our expert tips to ensure durability, efficiency, and peak performance…
If you’re a dedicated foodie, these fun facts you never knew about onions will definitely…